Key Benefits
- A straightforward and minimally painful procedure that addresses a significant aesthetic concern for many men
- Health insurance coverage is possible in cases involving glandular tissue, provided an endocrinological workup is negative
- We almost always combine liposuction with surgical gland removal to achieve the most harmonious and lasting results
What Is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is the abnormal enlargement of male breast tissue. It is a common and often distressing condition that can be treated effectively with surgery.
In most cases, gynecomastia results from a hormonal imbalance—a relative increase in estrogen (female hormones) or a decrease in testosterone (male hormones).
Possible causes include:
- Endocrine disorders (e.g., hyperthyroidism, Addison’s disease)
- Liver disease (especially alcoholic cirrhosis)
- Tumors of the testicles, lungs, or pituitary gland (e.g., prolactinoma)
- Use of certain medications, anabolic steroids, or cannabis
- General weight gain or obesity
Before any surgical intervention, a thorough clinical, hormonal, and radiological evaluation is essential to rule out a medical cause that may be managed non-surgically.
Types of Gynecomastia
- Glandular Gynecomastia: Excess glandular breast tissue
- Fatty Gynecomastia (Adipomastia): Purely fat-based enlargement, often associated with overall weight gain
- Mixed Gynecomastia: A combination of both fat and glandular tissue (most common)
Treatment Options
- Fatty Gynecomastia is treated with liposuction alone. Small cannulas are inserted via tiny incisions (typically two, under 4 mm) to remove fat.
- Glandular Gynecomastia requires surgical excision of the gland via a discreet trans-areolar incision (beneath the nipple).
- Mixed Gynecomastia combines both techniques: liposuction + gland removal through an incision hidden in the areola.
In rare and more severe cases, additional scars may be necessary:
- Periareolar scar: If the areola is very large (round-block technique)
- T-shaped or horizontal mastectomy scar: In cases of very large volume or sagging (ptosis)
Procedure Details
- Usually performed under general anesthesia
- In simpler cases, local anesthesia with sedation (neuroleptanalgesia) may be used
- Outpatient surgery (same-day discharge) is standard
- A special compression garment (Romeo by Medical Z) must be worn day and night for 15 days
- A pre-anesthesia consultation is required at least 48 hours before surgery
Avoid aspirin or similar medications for 10 days before the procedure
Frequently Asked Questions
What complications can occur?
- Hematoma (bleeding) may develop shortly after surgery and may require urgent drainage
- Lymphatic fluid buildup (seroma) can occur between day 5 and 15 post-op. If small, it can be monitored; if large, it may require a needle aspiration
- Temporary numbness of the nipple and areola area can last for up to 6 months
Is it a painful procedure?
Generally, no. However, moderate discomfort may be experienced in the first week, especially if extensive liposuction is performed.
When can I return to sports?
- Light activity like jogging can resume after 10 days
- Weight training or intense chest exercises should be avoided for at least 1 month
Is the surgery covered by health insurance?
Yes, if a glandular component is confirmed and a negative endocrinological evaluation has been completed.
Pure adipomastia (fat only) is not reimbursed by French health insurance.
What does gynecomastia surgery cost?
- If covered by health insurance: Our fees range from €2,500 to €4,000
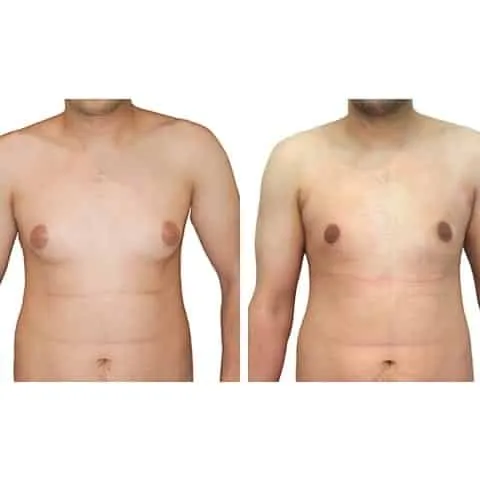
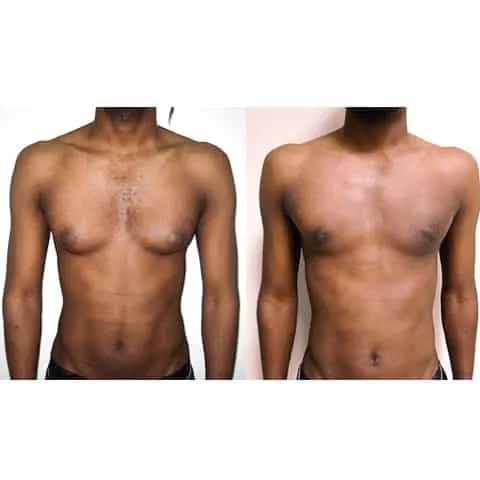
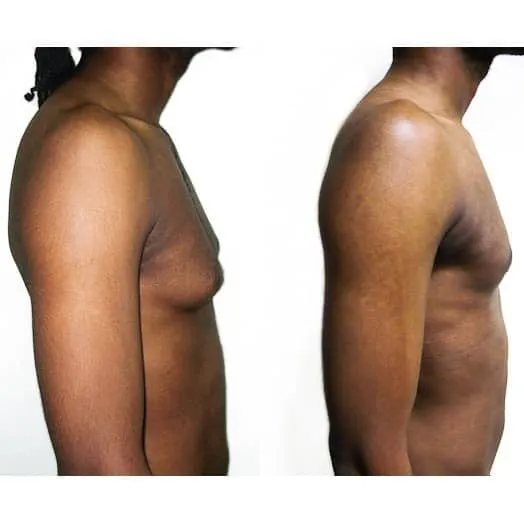
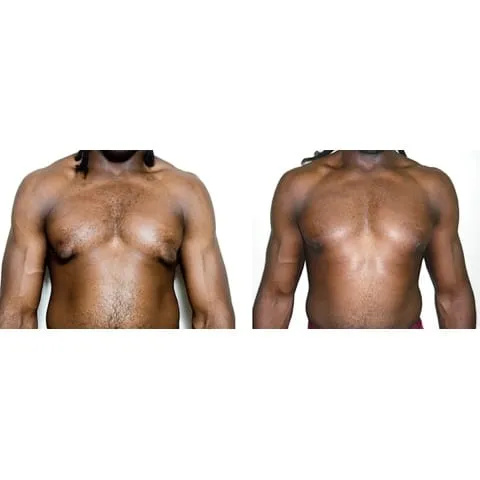
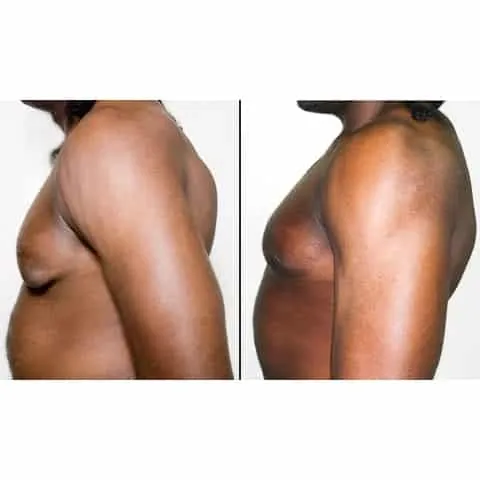
Photos des résultats d’une opération de gynécomastie à Paris
Découvrez les résultats avant-après d’une cure de gynécomastie réalisée par les Dr Berdah et Dr Benjoar dans leur cabinet médical à Paris.